

Windows API and GUI in safe, idiomatic Rust.
WinSafe has:
If you're looking for a comprehensive Win32 coverage, take a look at winapi or windows crates, which are unsafe, but have everything.
WinSafe documentation:
| Branch | Docs | | - | - | | Stable | docs.rs/winsafe | | Nightly (master) | rodrigocfd.github.io/winsafe/winsafe |
These are the estimated progresses of the GUI features:
| GUI feature | Estimated progress | | - | - | | User window/dialogs (main, modal and control) | 100% | | Native controls | 85% |
Plus, below are the numbers of native FFI items implemented:
| Native FFI item | Count | | - | - | | Functions | 586 | | Structs | 166 | | Constants | 11,990 | | Window messages | 648 | | Handles | 37 | | COM interfaces | 37 | | COM methods | 181 |
Add the dependency in your Cargo.toml:
toml
[dependencies]
winsafe = { version = "0.0.14", features = [] }
You can, alternatively, use the Nightly (master) branch directly, to get the latest features right away:
toml
[dependencies]
winsafe = { git = "https://github.com/rodrigocfd/winsafe", features = [] }
Then you must enable the Cargo features you want to be included – these modules are named after native Windows DLL and library names, mostly.
The following Cargo features are available so far:
| Feature | Description |
| - | - |
| advapi | Advapi32.dll, for Windows Registry |
| comctl | ComCtl32.dll, for Common Controls |
| comdlg | ComDlg32.dll, for the old Common Dialogs |
| dshow | DirectShow |
| gdi | Gdi32.dll, the Windows GDI |
| gui | The WinSafe high-level GUI abstractions |
| kernel | Kernel32.dll, all others will include it |
| ktm | Ktmw32.dll, the Kernel Transaction Manager |
| msimg | Msimg32.dll |
| ole | OLE and basic COM support |
| oleaut | OLE Automation |
| shell | Shell32.dll and Shlwapi.dll, the COM-based Windows Shell |
| user | User32.dll, the basic Windows GUI support |
| uxtheme | UxTheme.dll, extended window theming |
| version | Version.dll, to manipulate *.exe version info |
Note that a Cargo feature may depend on other features, which will be enabled automatically.
Note: You can find several examples in the dedicated repo: github.com/rodrigocfd/winsafe-examples
WinSafe allows you to create windows in two ways:
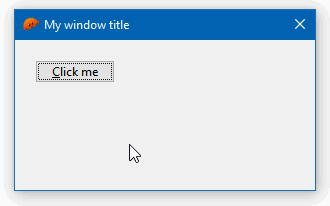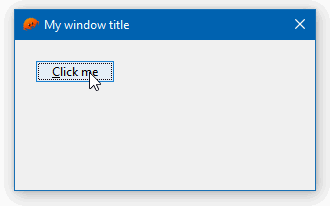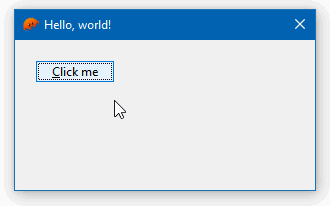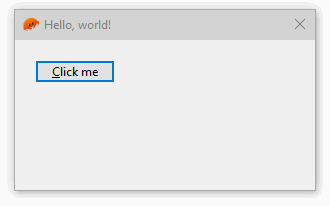
.res file created with a WYSIWYG resource editor.The example below creates a window with a button programmatically. Note how the click event is handled with a closure:
toml
[dependencies]
winsafe = { version = "0.0.14", features = ["gui"] }
```rust
use winsafe::prelude::*; use winsafe::{gui, POINT, SIZE};
fn main() { let my = MyWindow::new(); // instantiate our main window if let Err(e) = my.wnd.run_main(None) { // ... and run it eprintln!("{}", e); } }
pub struct MyWindow { wnd: gui::WindowMain, // responsible for managing the window btn_hello: gui::Button, // a button }
impl MyWindow { pub fn new() -> Self { let wnd = gui::WindowMain::new( // instantiate the window manager gui::WindowMainOpts { title: "My window title".to_owned(), size: (300, 150), ..Default::default() // leave all other options as default }, );
let btn_hello = gui::Button::new(
&wnd, // the window manager is the parent of our button
gui::ButtonOpts {
text: "&Click me".to_owned(),
position: (20, 20),
..Default::default()
},
);
let new_self = Self { wnd, btn_hello };
new_self.events(); // attach our events
new_self
}
fn events(&self) {
let wnd = self.wnd.clone(); // clone so it can be passed into the closure
self.btn_hello.on().bn_clicked(move || {
wnd.hwnd().SetWindowText("Hello, world!")?;
Ok(())
});
}
} ```
Licensed under MIT license, see LICENSE.md for details.