https://github.com/zBaitu/rsfmt
Active again from old repo: rfmt
rsfmt is a Rust source code formatter. Yes, there is already an official tool rustfmt. So why write another one?
Support for Rust 1.60 nightly
cargo install rsfmt
git clone git@github.com:zBaitu/rsfmt.git
cargo build --release
``` rsfmt 1.60.0
USAGE: rsfmt [FLAGS] [input]
FLAGS: -a, --ast Prints the rust original syntax ast debug info -c, --check Only check without output or overwrite -d, --debug Prints the rsfmt ir debug info -h, --help Prints help information -k, --keep Keep going when error occurred -o, --overwrite Overwrite the source file -p, --print Prints the rsfmt ir simple format -V, --version Prints version information
ARGS:
Input file or dir. If input is a dir, rsfmt will do action for all files in this dir recursively.
If neither options nor input is specified, rsfmt will format source code from stdin
```
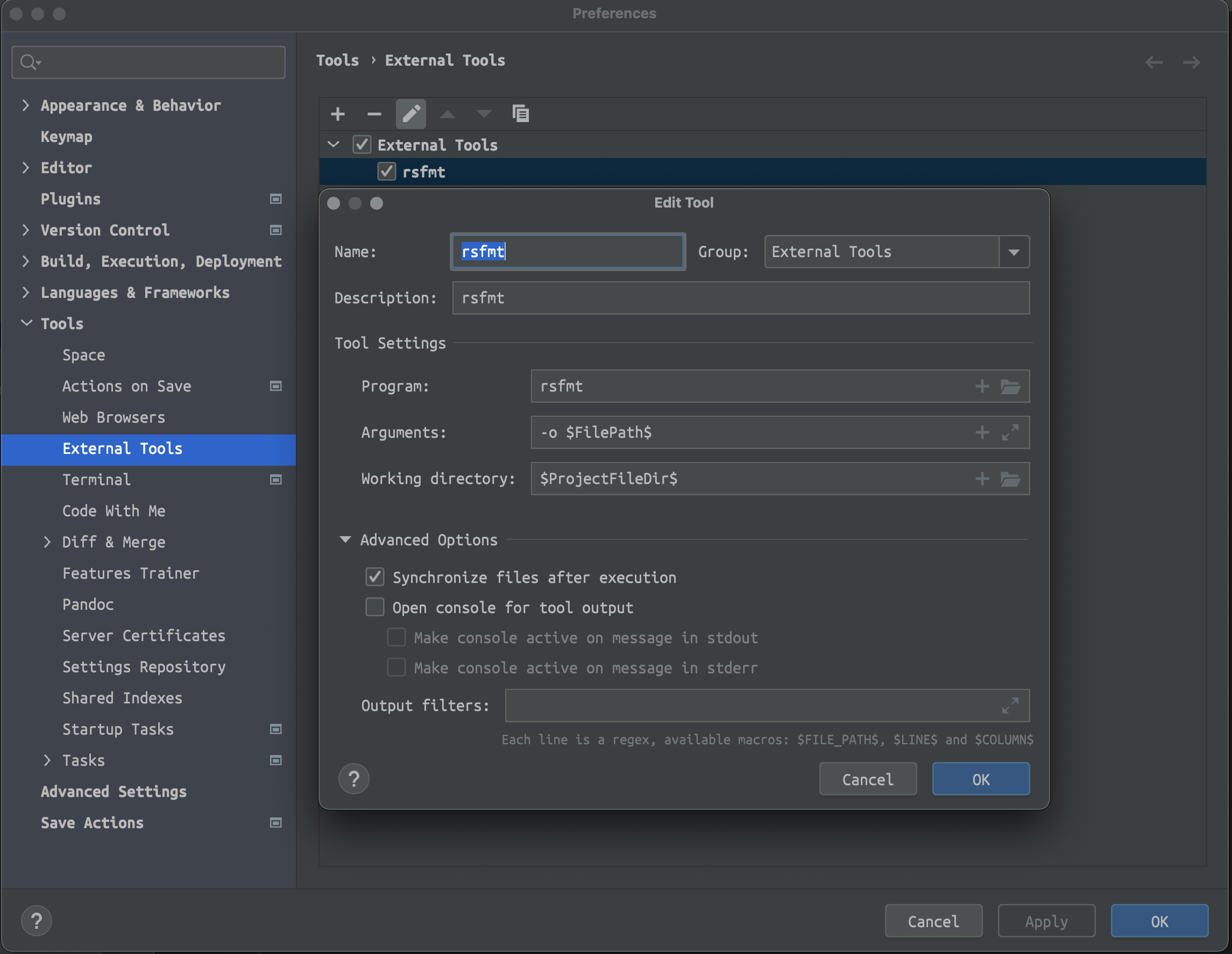
In fact, I only use rsfmt with IntelliJ now. Just add an external tool as below.

Other editor usage can access
to Running Rustfmt from your editor. I think
maybe just replace the rustfmt to rsfmt.
Comparing to rustfmt, there are some main different features from rsfmt:
crate, use, mod, attributes and sort them.doc, comment, string. You can use the check function to show exceed lines and trailing
white space lines.The following part will show such features in detail, with some existing issues from rustfmt.
For the issue: rustfmt reformats bit manipiulations.
fn main() {
let (a, b, c, d) = (0, 0, 0, 0);
let _ = u32::from_be(((a as u32) << 24) |
((b as u32) << 16) |
((c as u32) << 8) |
(d as u32) << 0);
}
fn main() {
let (a, b, c, d) = (0, 0, 0, 0);
let _ =
u32::from_be(((a as u32) << 24) | ((b as u32) << 16) | ((c as u32) << 8) | (d as u32) << 0);
}
Of course, you can use #[rustfmt_skip] to avoid such code, but in my personal opinon, I really don't like to add other
code just for the source formatting tool.
fn main() {
let (a, b, c, d) = (0, 0, 0, 0);
let _ = u32::from_be(((a as u32) << 24) |
((b as u32) << 16) |
((c as u32) << 8) |
(d as u32) << 0);
}
It looks OK, isn't it? Why rsfmt can keep the user wrap? Because of the rsfmt ir. The custom ir of Rust AST record location information of every element as far as possible. Look another example:
fn main() {
let ref_packet = [0xde, 0xf0, 0x12, 0x34, 0x45, 0x67,
0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78, 0x9a, 0xbc,
0x86, 0xdd];
}
fn main() {
let ref_packet = [
0xde, 0xf0, 0x12, 0x34, 0x45, 0x67, 0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78, 0x9a, 0xbc, 0x86, 0xdd,
];
}
fn main() {
let ref_packet = [0xde, 0xf0, 0x12, 0x34, 0x45, 0x67,
0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78, 0x9a, 0xbc,
0x86, 0xdd];
}
I prefer to put parameters on one line as much as possible.
fn main() {
f(123456789, "abcdefg", "hijklmn", 0987654321, "opqrst", "uvwxyz", 123456789, "abcdefg", "hijklmn", 0987654321, "opqrst", "uvwxyz");
}
fn main() {
f(
123456789, "abcdefg", "hijklmn", 0987654321, "opqrst", "uvwxyz", 123456789, "abcdefg",
"hijklmn", 0987654321, "opqrst", "uvwxyz",
);
}
fn main() {
f(123456789, "abcdefg", "hijklmn", 0987654321, "opqrst", "uvwxyz", 123456789, "abcdefg", "hijklmn", 0987654321,
"opqrst", "uvwxyz");
}
If the left align position is beyond limit(It is 40 for now), rsfmt prefer double indent align to function call align. rsfmt make source code left lean, while rustfmt is right lean, I think. An exsiting issue: rustfmt should avoid rightwards drifting big blocks of code
```` fn main() { let mut arms = variants.iter().enumerate().map(|(i, &(ident, vspan, ref summary))| { let iexpr = cx.exprusize(vspan, i); let pat = cx.patlit(vspan, i_expr);
let path = cx.path(v_span, vec![substr.type_ident, ident]);
let thing = rand_thing(cx, v_span, path, summary, |cx, sp| rand_call(cx, sp));
cx.arm(v_span, vec![ pat ], thing)
}).collect::<Vec<ast::Arm> >();
} ````
``` fn main() { let mut arms = variants .iter() .enumerate() .map(|(i, &(ident, vspan, ref summary))| { let iexpr = cx.exprusize(vspan, i); let pat = cx.patlit(vspan, i_expr);
let path = cx.path(v_span, vec![substr.type_ident, ident]);
let thing = rand_thing(cx, v_span, path, summary, |cx, sp| rand_call(cx, sp));
cx.arm(v_span, vec![pat], thing)
})
.collect::<Vec<ast::Arm>>();
} ```
fn main() {
let mut arms = variants.iter().enumerate().map(|(i, &(ident, v_span, ref summary))| {
let i_expr = cx.expr_usize(v_span, i);
let pat = cx.pat_lit(v_span, i_expr);
let path = cx.path(v_span, vec![substr.type_ident, ident]);
let thing = rand_thing(cx, v_span, path, summary, |cx, sp| rand_call(cx, sp));
cx.arm(v_span, vec![pat], thing)
}).collect::<Vec<ast::Arm>>();
}
The result from rsfmt is not changed, because this source code fits rsfmt's code style.
crate, use, mod, attributes and sort them```
extern crate rst; extern crate getopts; extern crate walkdir;
use std::env; use getopts::Options;
mod ts;
mod ir; mod ft; mod tr; mod rsfmt; ```
```
extern crate getopts; extern crate rst; extern crate walkdir;
use getopts::Options; use std::env;
mod ts;
mod ft; mod ir; mod rsfmt; mod tr; ```
rsfmt only group items that appear continuously. If on item is special that it must keep its order, like the mod ts;,
make it separate from others.
doc, comment, stringThere are many issues about doc, comment, string, raw string from rustfmt. I think such element can leave free for user to write anything, any format they want.
If you want to check is there some line break the code style limit, rsfmt provide check function.
// aaaaa
// bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
fn main() {
let a = r#"aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb"#;
}
``` rsfmt -c g.rs
"g.rs" trailingwslines: {1, 4} ````
You can check or overwrite all files in a directory.
rsfmt -c rust/src/libcore
rsfmt -o rust/src/libstd
Maybe you are interested to see the Rust AST of a source code.
// AST
fn main() {}
rsfmt -a a.rs
``` Crate { attrs: [], items: [ Item { attrs: [], id: NodeId(4294967040), span: Span { lo: BytePos( 7, ), hi: BytePos( 19, ), ctxt: #0, }, vis: Visibility { kind: Inherited, span: Span { lo: BytePos( 7, ), hi: BytePos( 7, ), ctxt: #0, }, tokens: None, }, ident: main#0, kind: Fn( FnKind( Final, FnSig { header: FnHeader { unsafety: No, asyncness: No, constness: No, ext: None, }, decl: FnDecl { inputs: [], output: Default( Span { lo: BytePos( 17, ), hi: BytePos( 17, ), ctxt: #0, }, ), }, span: Span { lo: BytePos( 7, ), hi: BytePos( 16, ), ctxt: #0, }, }, Generics { params: [], whereclause: WhereClause { haswheretoken: false, predicates: [], span: Span { lo: BytePos( 16, ), hi: BytePos( 16, ), ctxt: #0, }, }, span: Span { lo: BytePos( 14, ), hi: BytePos( 14, ), ctxt: #0, }, }, Some( Block { stmts: [], id: NodeId(4294967040), rules: Default, span: Span { lo: BytePos( 17, ), hi: BytePos( 19, ), ctxt: #0, }, tokens: None, }, ), ), ), tokens: None, }, ], span: Span { lo: BytePos( 7, ), hi: BytePos( 19, ), ctxt: #0, }, procmacros: [], }
0: Isolated [ "// AST", ] ```
As rsfmt is written as a personal tool(toy) for my daily develop, it lacks some common features now.
``` // aaaaa
// bbbbb struct A { // ccccc-DISAPPEARED // ddddd a: bool, // eeeee b: i32, // ffff // ggggg } // hhhhh
// iiiii fn f(a: bool, /* jjjjj-DISAPPEARED / b: i32, / kkkkk-DISAPPEARED */) -> bool { // lllll-DISAPPEARED // mmmmm const b: bool = false; // nnnnn let mut a = true; // ooooo a = false; // ppppp a!();// qqqqq a // rrrrr } // sssss // ttttt
// uuuuu ```
``` // aaaaa
// bbbbb struct A { // ddddd a: bool, // eeeee b: i32, // ffff // ggggg } // hhhhh
// iiiii fn f(a: bool, b: i32) -> bool { // mmmmm const b: bool = false; // nnnnn let mut a = true; // ooooo a = false; // ppppp a!(); // qqqqq a // rrrrr } // sssss // ttttt
// uuuuu ```