This program aims to collect Linux system information including hostname, kernel version, uptime, RTC time, load average, CPU, memory, network interfaces and block devices. It can be used not only as a normal CLI tool, but also a web application with a front-end webpage and useful HTTP APIs.
``` EXAMPLES: mprober hostname # Show the hostname mprober kernel # Show the kernel version mprober uptime # Show the uptime mprober uptime -m # Show the uptime and refresh every second mprober uptime -p # Show the uptime without colors mprober uptime -l # Show the uptime with darker colors (fitting in with light themes) mprober uptime -s # Show the uptime in seconds mprober time # Show the RTC (UTC) date and time mprober time -m # Show the RTC (UTC) date and time and refresh every second mprober time -p # Show the RTC (UTC) date and time without colors mprober time -l # Show the RTC (UTC) date and time with darker colors (fitting in with light themes) mprober cpu # Show load average and current CPU stats on average mprober cpu -m 1000 # Show load average and CPU stats on average and refresh every 1000 milliseconds mprober cpu -p # Show load average and current CPU stats on average without colors mprober cpu -l # Show load average and current CPU stats on average with darker colors (fitting in with light themes) mprober cpu -s # Show load average and current stats of CPU cores separately mprober cpu -i # Only show CPU information mprober memory # Show current memory stats mprober memory -m 1000 # Show memory stats and refresh every 1000 milliseconds mprober memory -p # Show current memory stats without colors mprober memory -l # Show current memory stats with darker colors (fitting in with light themes) mprober memory -u kb # Show current memory stats in KB mprober network # Show current network stats mprober network -m 1000 # Show network stats and refresh every 1000 milliseconds mprober network -p # Show current network stats without colors mprober network -l # Show current network stats with darker colors (fitting in with light themes) mprober network -u kb # Show current network stats in KB mprober volume # Show current volume stats mprober volume -m 1000 # Show current volume stats and refresh every 1000 milliseconds mprober volume -p # Show current volume stats without colors mprober volume -l # Show current volume stats without colors mprober volume -u kb # Show current volume stats in KB mprober volume -i # Only show volume information without I/O rates mprober volume --mounts # Show current volume stats including mount points mprober web # Start a HTTP service on port 8000 to monitor this computer. The default time interval is 3 seconds mprober web -m 2 # Start a HTTP service on port 8000 to monitor this computer. The time interval is set to 2 seconds mprober web -p 7777 # Start a HTTP service on port 7777 to monitor this computer mprober web -a auth_key # Start a HTTP service on port 8000 to monitor this computer. APIs need to be invoked with an auth key mprober web --only-api # Start a HTTP service on port 8000 to serve only HTTP APIs mprober benchmark # Run benchmarks mprober benchmark --disable-cpu # Run benchmarks except for benchmarking CPU mprober benchmark --enable-memory # Benchmark the memory
USAGE: mprober [SUBCOMMAND]
FLAGS: -h, --help Prints help information -V, --version Prints version information
SUBCOMMANDS: hostname Shows the hostname kernel Shows the kernel version uptime Shows the uptime time Shows the RTC (UTC) date and time cpu Shows CPU stats memory Shows memory stats network Shows network stats volume Shows volume stats web Starts a HTTP service to monitor this computer benchmark Runs benchmarks to measure the performance of this environment help Prints this message or the help of the given subcommand(s) ```
From crates.io,
```bash cargo install mprober
```
From GitHub (x86 and x86_64),
```bash (curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/magiclen/m-prober/releases/latest | sed -r -n 's/."browser_download_url": *"(.\/mprober'$(uname -m)')".*/\1/p' | wget -i -) && sudo mv mprober$(uname -m) /usr/local/bin/mprober && sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/mprober
```
bash
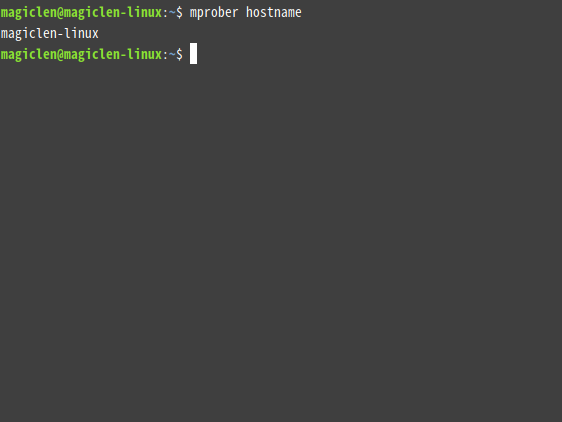
mprober hostname
In addition to hostname, h, host, name, and servername are also acceptable.
bash
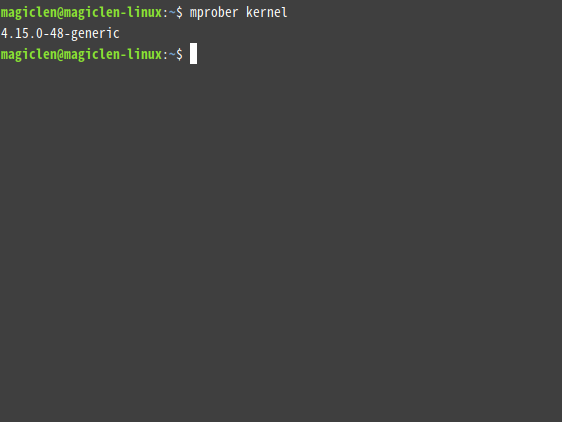
mprober kernel
In addition to kernel, k, l, and linux are also acceptable.
bash
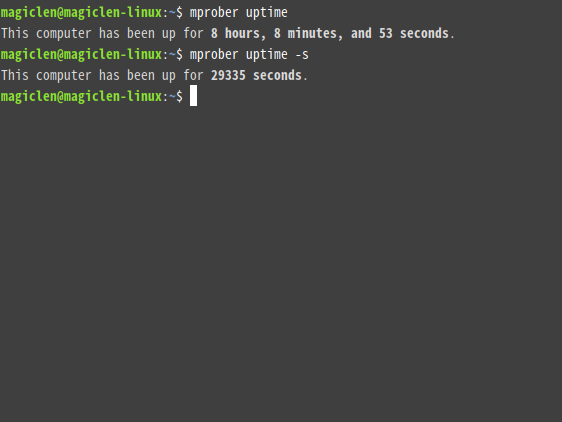
mprober uptime
In addition to uptime, u, up, utime, and ut are also acceptable.
bash
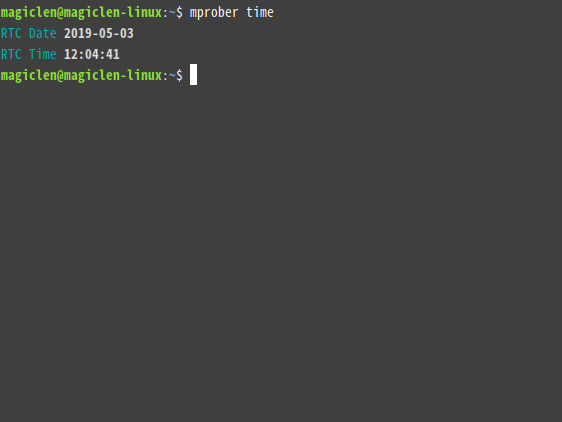
mprober time
In addition to time, t, systime, stime, st, utc, utctime, rtc, rtctime, and date are also acceptable.
bash
mprober cpu
In addition to cpu, c, cpus, core, cores, load, processor, and processors are also acceptable.
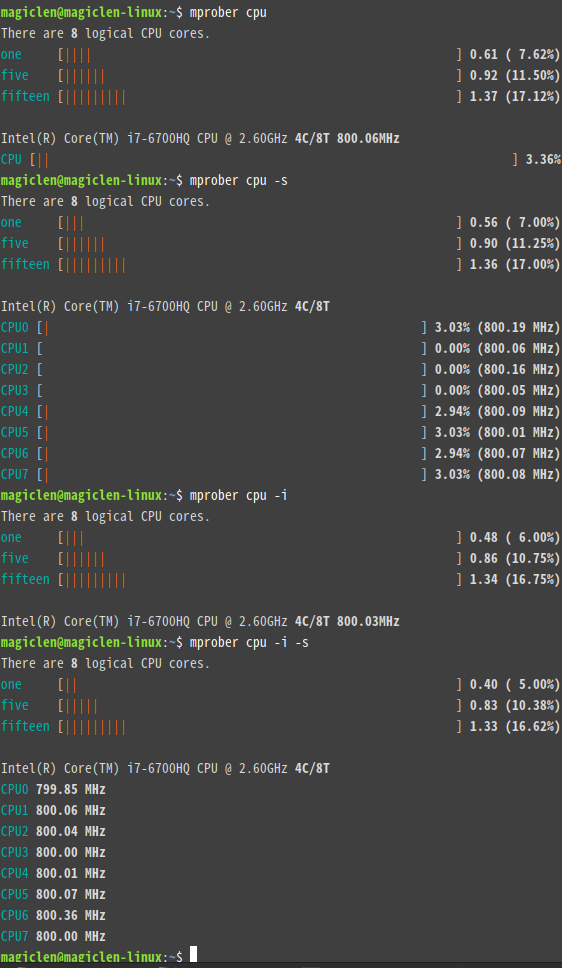
bash
mprober memory
In addition to memory, m, mem, f,free, memories, swap, ram, dram, ddr, cache, buffer, buffers, buf, and buff are also acceptable.
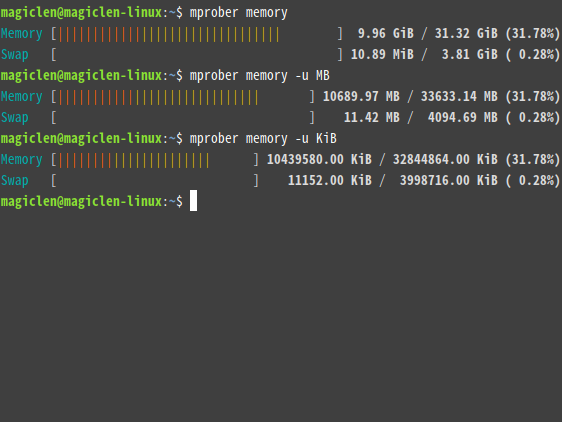
bash
mprober network
In addition to network, n, net, networks,bandwidth, and traffic are also acceptable.
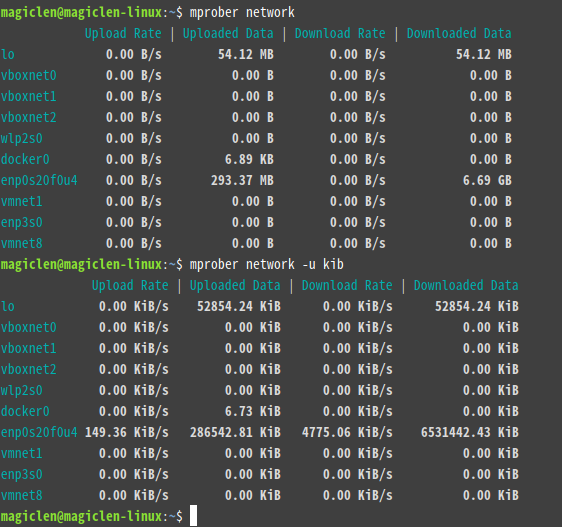
bash
mprober volume
In addition to volume, v, storage, volumes, d, disk, disks, blk, block, blocks, mount, mounts, ssd, and hdd are also acceptable.
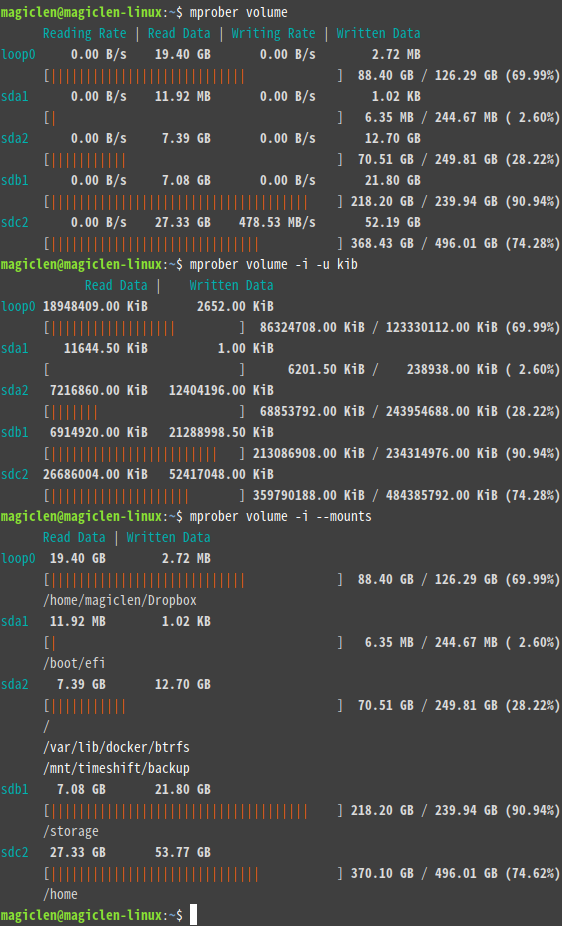
Environment variables, MPROBER_LIGHT and MPROBER_FORCE_PLAIN can be used to control the output colors.
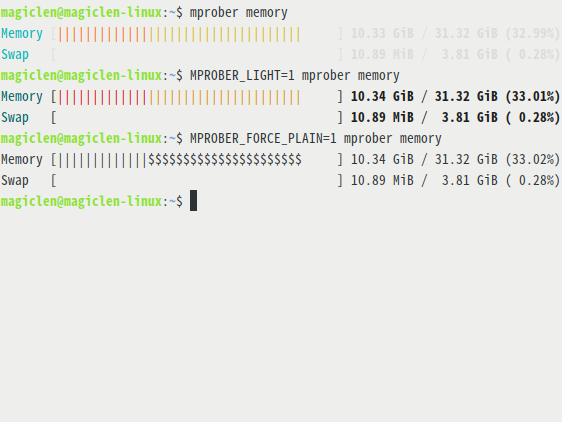
bash
mprober web
In addition to web, w, server, and http are also acceptable.
Once you start the server, you can open http://0.0.0.0:8000 via a web browser such as Firefox or Chrome.
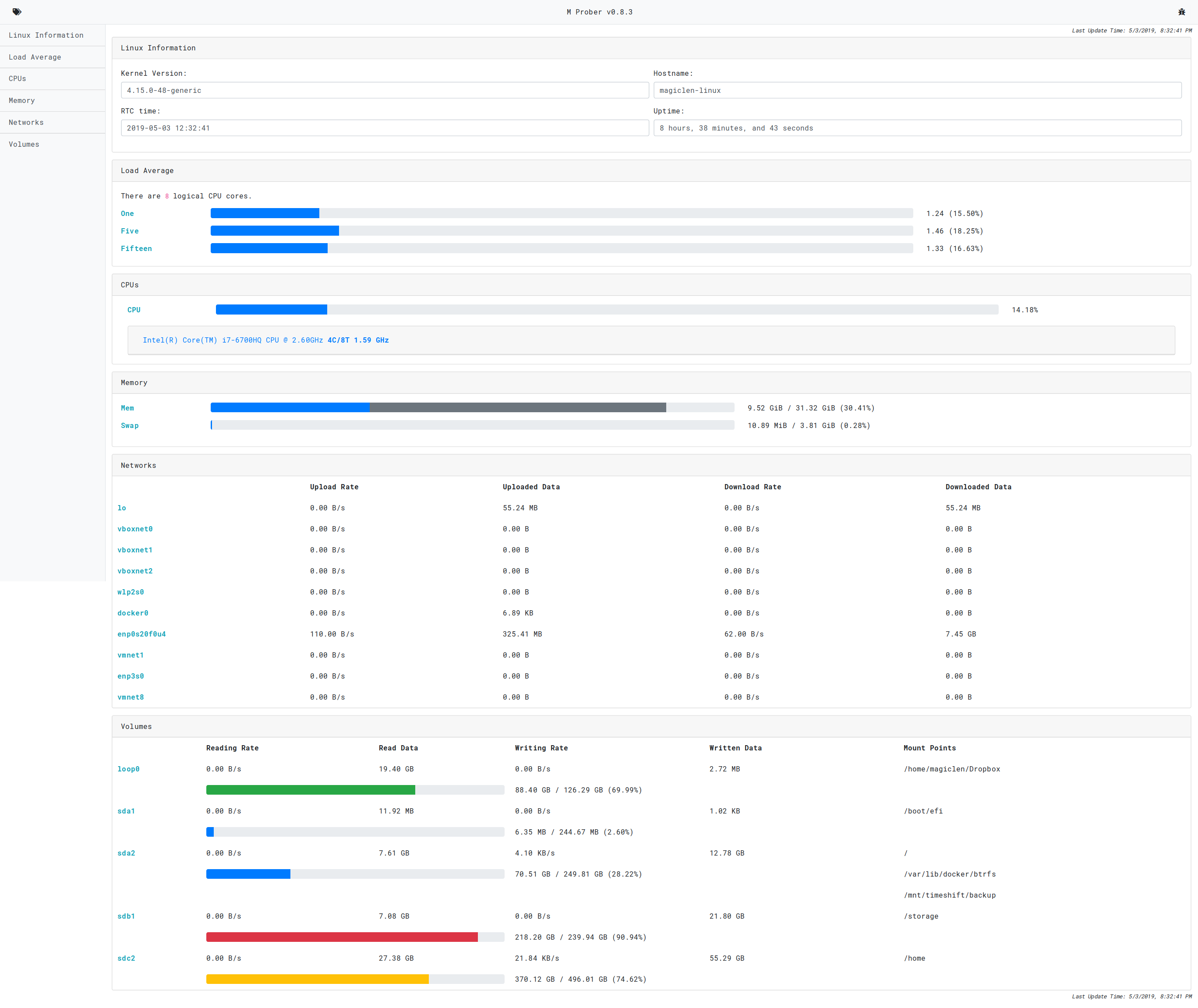
To change the listening port, use the -p <port> option. To change the detecting time interval, use the -m <SECONDS> option, where the <SECONDS> is ranged from 1 to 15.
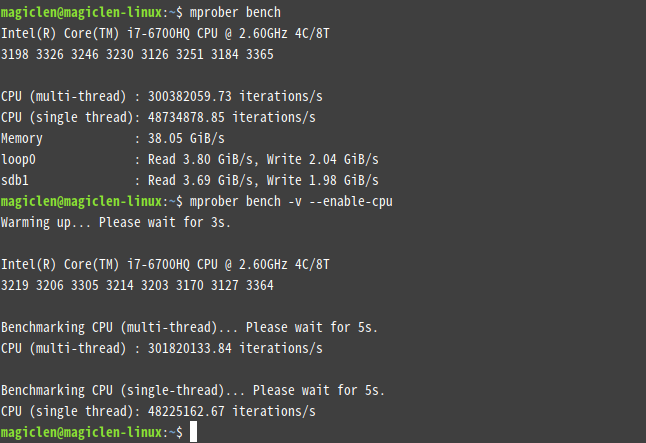
To benchmark the performance of CPU, memory and volumes,
bash
mprober benchmark
In addition to benchmark, b, bench, and performance are also acceptable.
Adding the --disable-xxx or --enable-xxx flags can control what benchmarks you want to run.
/api/hostnamejson
{
"code": 0,
"data": "magiclen-linux"
}
/api/kerneljson
{
"code": 0,
"data": "4.15.0-48-generic"
}
/api/uptimejson
{
"code": 0,
"data": 31694
}
The unit of data is seconds.
/api/timejson
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"date": "2019-05-03",
"time": "12:43:14"
}
}
It's RTC time.
/api/cpujson
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"cpus": [
{
"cores": 4,
"mhz": [
2571.96,
2688.208,
2604.095,
2700.238,
2700.034,
2699.908,
2700.329,
2699.986
],
"model_name": "Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700HQ CPU @ 2.60GHz",
"threads": 8
}
],
"load_average": {
"fifteen": 1.02,
"five": 0.83,
"one": 0.61
}
}
}
/api/cpu-detectjson
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"cpus": [
{
"cores": 4,
"mhz": [
1808.254,
1787.732,
1430.044,
1845.768,
1751.993,
1751.121,
1769.048,
1663.091
],
"model_name": "Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700HQ CPU @ 2.60GHz",
"threads": 8
}
],
"cpus_stat": [
0.08386009270965024,
0.09152542372881356,
0.10472972972972971,
0.11295681063122924,
0.06418918918918919,
0.09364548494983276,
0.06397306397306397,
0.053691275167785234,
0.0821917808219178
],
"load_average": {
"fifteen": 1.02,
"five": 0.84,
"one": 0.74
}
}
}
The first value in the cpus_stat field is the average usage of each cores. The remaining values are the usage for each logical CPU core.
/api/memoryjson
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"memory": {
"available": 22659469312,
"buffers": 10412032,
"cache": 19094446080,
"free": 4154060800,
"shared": 119246848,
"total": 33633140736,
"used": 10374221824
},
"swap": {
"cache": 385024,
"free": 4082888704,
"total": 4094685184,
"used": 11411456
}
}
}
The unit of numbers is bytes.
/api/network-detectjson
{
"code": 0,
"data": [
{
"download_rate": 0.0,
"download_total": 55713769,
"interface": "lo",
"upload_rate": 0.0,
"upload_total": 55713769
},
{
"download_rate": 702.0,
"download_total": 7461474545,
"interface": "enp0s20f0u4",
"upload_rate": 1280.6666666666667,
"upload_total": 331829069
}
]
}
The unit of totals is bytes. The unit of rates is bytes/second.
/api/volumejson
{
"code": 0,
"data": [
{
"device": "sda2",
"mount_points": [
"/",
"/var/lib/docker/btrfs"
],
"read_total": 7612149760,
"size": 249809600512,
"used": 70506823680,
"write_total": 12919939072
},
{
"device": "sdb1",
"mount_points": [
"/storage"
],
"read_total": 7080878080,
"size": 239938535424,
"used": 218200993792,
"write_total": 21799934464
},
{
"device": "sdc2",
"mount_points": [
"/home"
],
"read_total": 27511930880,
"size": 496011051008,
"used": 370128474112,
"write_total": 56615944192
}
]
}
The unit of totals is bytes.
/api/volume-detectjson
{
"code": 0,
"data": [
{
"device": "sda2",
"mount_points": [
"/",
"/var/lib/docker/btrfs"
],
"read_rate": 0.0,
"read_total": 7612149760,
"size": 249809600512,
"used": 70506823680,
"write_rate": 0.0,
"write_total": 12928978944
},
{
"device": "sdb1",
"mount_points": [
"/storage"
],
"read_rate": 0.0,
"read_total": 7080878080,
"size": 239938535424,
"used": 218200993792,
"write_rate": 0.0,
"write_total": 21799934464
},
{
"device": "sdc2",
"mount_points": [
"/home"
],
"read_rate": 0.0,
"read_total": 27511934976,
"size": 496011051008,
"used": 370131861504,
"write_rate": 4965717.333333333,
"write_total": 56771334144
}
]
}
The unit of totals is bytes. The unit of rates is bytes/second.
/api/alljson
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"cpus": [
{
"cores": 4,
"mhz": [
1200.121,
1200.272,
1200.12,
1200.055,
1200.098,
1200.034,
1200.014,
1200.124
],
"model_name": "Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700HQ CPU @ 2.60GHz",
"threads": 8
}
],
"cpus_stat": [
0.04951741502308015,
0.043333333333333335,
0.030405405405405407,
0.05743243243243243,
0.056666666666666664,
0.04983388704318937,
0.05387205387205387,
0.05405405405405406,
0.05067567567567568
],
"hostname": "magiclen-linux",
"kernel": "4.15.0-48-generic",
"load_average": {
"fifteen": 0.8,
"five": 0.53,
"one": 0.28
},
"memory": {
"available": 22578839552,
"buffers": 10412032,
"cache": 19104878592,
"free": 4062957568,
"shared": 119230464,
"total": 33633140736,
"used": 10454892544
},
"network": [
{
"download_rate": 0.0,
"download_total": 55798721,
"interface": "lo",
"upload_rate": 0.0,
"upload_total": 55798721
},
{
"download_rate": 9.333333333333334,
"download_total": 7463048290,
"interface": "enp0s20f0u4",
"upload_rate": 28.666666666666668,
"upload_total": 333465932
}
],
"rtc_time": {
"date": "2019-05-03",
"time": "12:54:34"
},
"swap": {
"cache": 385024,
"free": 4082888704,
"total": 4094685184,
"used": 11411456
},
"uptime": 32437,
"volumes": [
{
"device": "sda2",
"mount_points": [
"/",
"/var/lib/docker/btrfs"
],
"read_rate": 0.0,
"read_total": 7612149760,
"size": 249809600512,
"used": 70506831872,
"write_rate": 0.0,
"write_total": 12939075584
},
{
"device": "sdb1",
"mount_points": [
"/storage"
],
"read_rate": 0.0,
"read_total": 7080878080,
"size": 239938535424,
"used": 218200993792,
"write_rate": 0.0,
"write_total": 21799934464
},
{
"device": "sdc2",
"mount_points": [
"/home"
],
"read_rate": 0.0,
"read_total": 27521441792,
"size": 496011051008,
"used": 370118373376,
"write_rate": 744106.6666666666,
"write_total": 56883159040
}
]
}
}
If you need expose above HTTP APIs to the Internet. In order to prevent these APIs from being invoked by anyone, you can enable a simple authorization mechanism that is built in this program.
When starting the HTTP server from CLI, you can add a -a <AUTH_KEY> option. Then, every API needs to be invoked by a request which contains a Authorization header to send the AUTH_KEY.
Also, you may want to disable the web page. Just add a --only-api flag.
ps command)top command)