


Hotline is a graphics engine and live coding tool that allows you to edit code, shaders, and render configs without restarting the application. It provides a client application which remains running for the duration of a session. Code can be reloaded that is inside the dynamic plugins and render configs can be edited and hot reloaded through pmfx files.
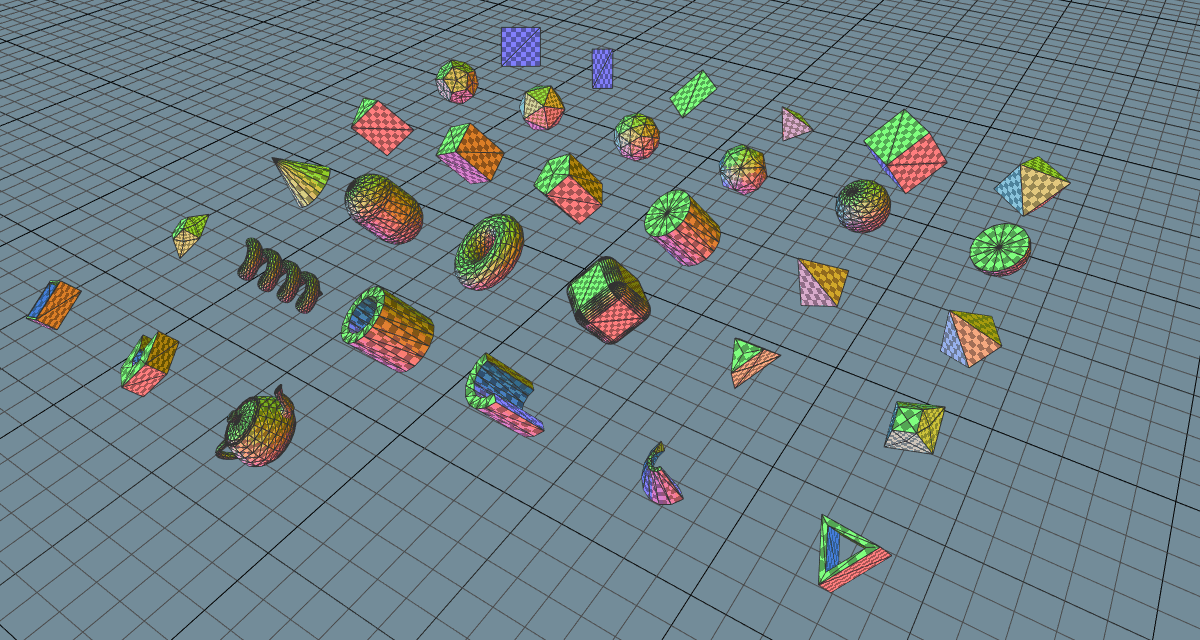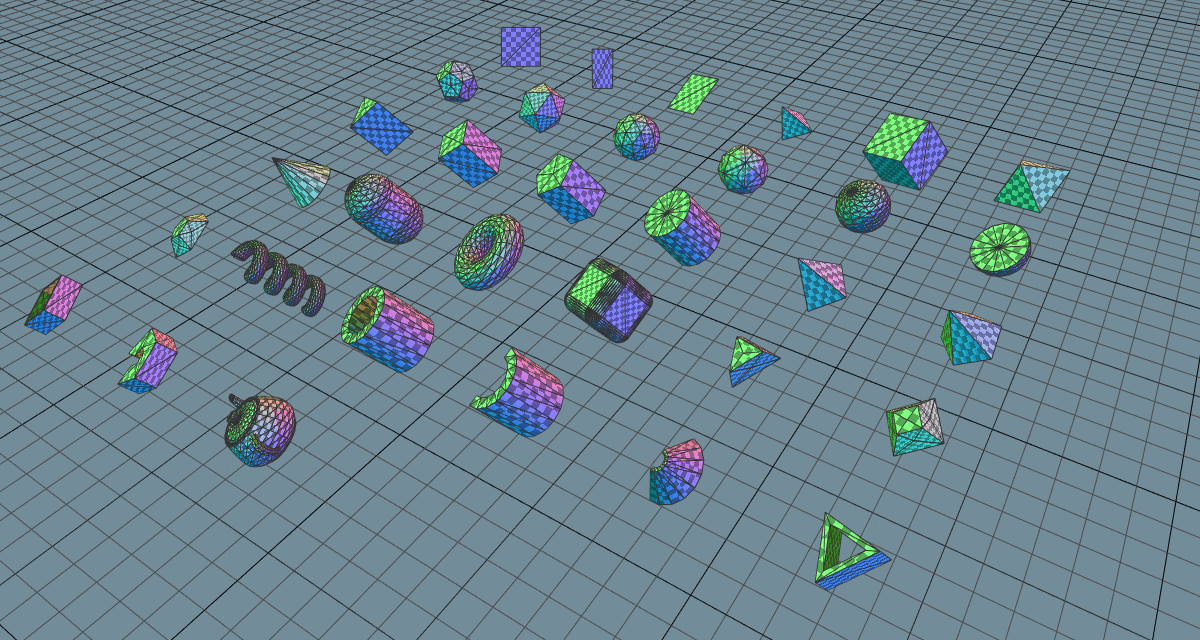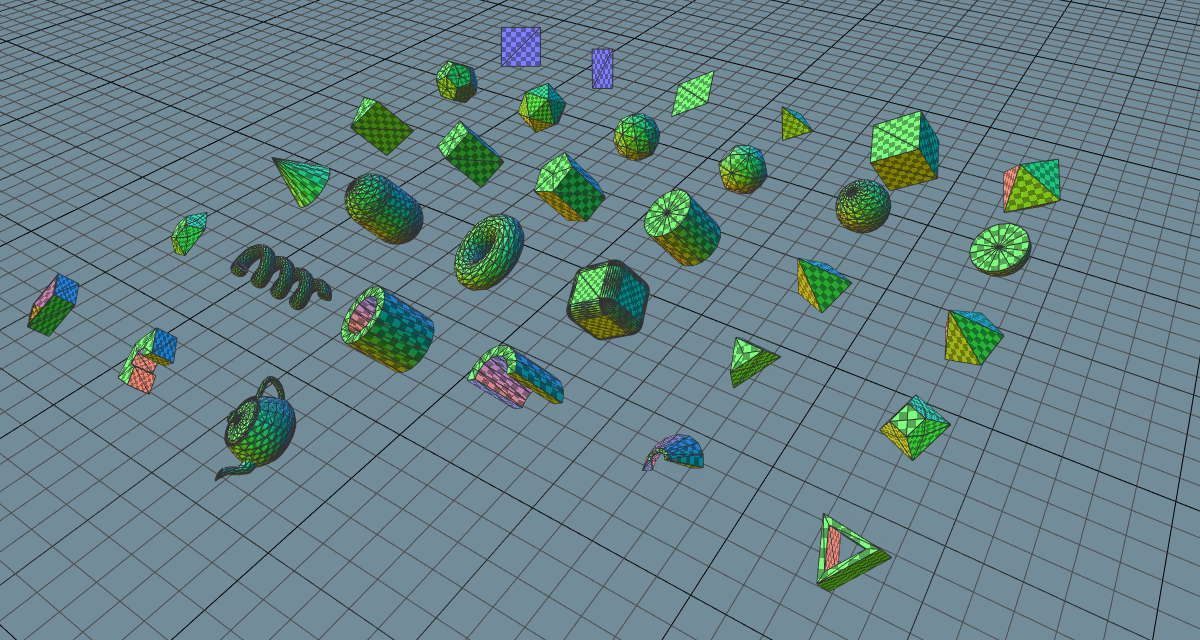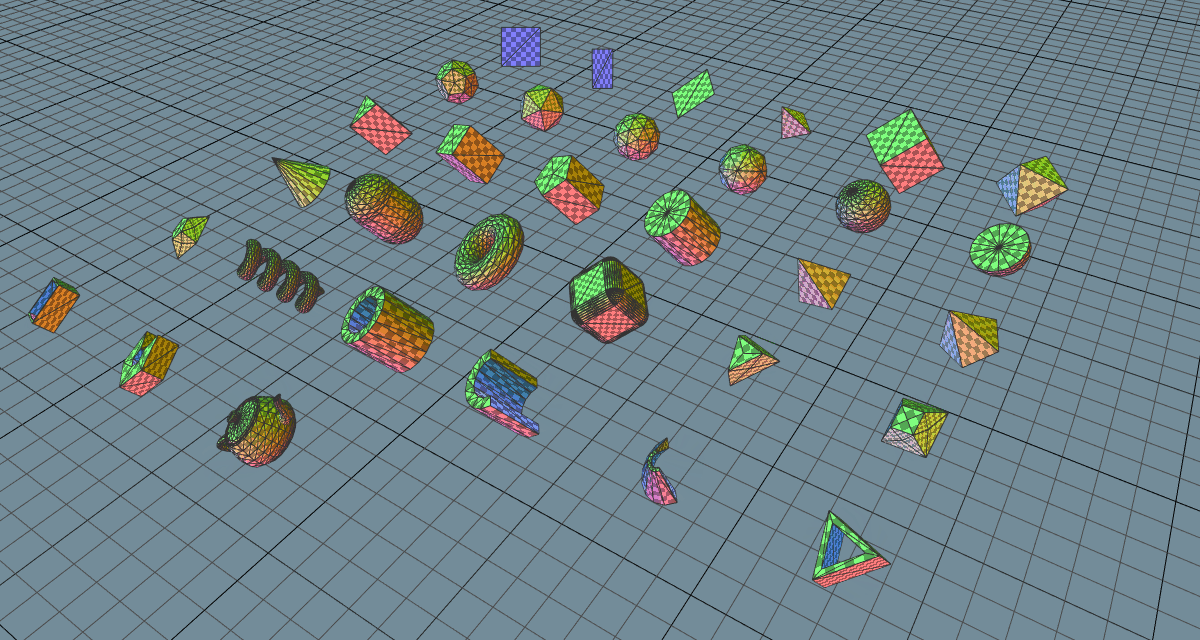
There is a demo video showcasing the features in their early stages and an example workflow demonstration of how the geometry primitives were created. Some development has been live streamed on Twitch and archived on YouTube.
Currently Windows with Direct3D12 is the only supported platform, there are plans for macOS, Metal, Linux, Vulkan and more over time.
For the time being it is recommended to use the repository from GitHub if you want to use the example plugins or standalone examples. If you just want to use the library then crates.io is suitable. There are some difficulties with publishing data and plugins which I hope to iron out in time.
The hotline-data repository is required to build and serve data for the examples and the example plugins, it is included as a submodule of this repository, you can clone with submodules as so:
git clone https://github.com/polymonster/hotline.git --recursive
You can add the submodule after cloning or update the submodule to keep it in-sync with the main repository as follows:
git submodule update --init --recursive
You can run the binary client which allows code to be reloaded through plugins. There are some plugins already provided with the repository:
```text // build the hotline library and the client, fetch the hotline-data repository cargo build
// build the data .\hotline-data\pmbuild.cmd win32-data
// then build plugins cargo build --manifest-path plugins/Cargo.toml
// run the client cargo run client ```
Any code changes made to the plugin libs will cause a rebuild and reload to happen with the client still running. You can also edit the shaders where hlsl files make up the shader code and pmfx files allow you to specify pipeline state objects in config files. Any changes detected to pmfx shaders will be rebuilt and all modified pipelines or views will be rebuilt.
To make things more convenient during development and keep the plugins, client and lib all in sync and make switching configurations easily, you can use the bundled pmbuild in the hotline-data repository and use the following commands which bundle together build steps:
```text // show aavailable build profiles .hotline-datapmbuild.cmd -help
// build release .hotline-datapmbuild.cmd win32-release
// build debug .hotline-datapmbuild.cmd win32-debug
// run the client .hotline-datapmbuild.cmd win32-debug -run
// build and run the client .hotline-datapmbuild.cmd win32-release -all -run ```
Because hotline is still in it's infancy things are changing quickly and pmfx-shader is rapidly evolving to assist the needs of new graphics features. In order to make this possible I have been swoitching between a pre-built release and a development version. If you see an error message such as this:
The system cannot find the path specified. [error] processing task pmfx ```
This means pmfx has been comitted in dev mode, you can edit the config.jsn to switch the pmfx task type from type: pmfx_dev back to type: pmfx or comment out that line completely. If you do need the pmfx_dev unctionality you can clone the pmfx-shader repository so it is adjacent to the hotline directory.
There are included tasks and launch files for vscode including configurations for the client and the examples. Launching the client from vscode in debug or release will build the core hotline lib, client, data and plugins.
Plugins are loaded by passing a directory to addpluginlib which contains a Cargo.toml and is a dynamic library. They can be opened interactively in the client using the File > Open from the main menu bar by selecting the Cargo.toml.
The basic Cargo.toml setup looks like this:
```toml [package] name = "ecs_demos" version = "0.1.0" edition = "2021"
[lib] crate-type = ["rlib", "dylib"]
[dependencies] hotline-rs = { path = "../.." } ```
You can provide your own plugin implementations using the Plugin trait. A basic plugin can hook itself by implementing a few functions:
```rust
impl Plugin
fn setup(&mut self, client: Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App>)
-> Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App> {
println!("plugin setup");
client
}
fn update(&mut self, client: client::Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App>)
-> Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App> {
println!("plugin update");
client
}
fn unload(&mut self, client: Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App>)
-> Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App> {
println!("plugin unload");
client
}
fn ui(&mut self, client: Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App>)
-> Client<gfx_platform::Device, os_platform::App> {
println!("plugin ui");
client
}
}
// the macro instantiates the plugin with a c-abi so it can be loaded dynamically. hotline_plugin![EmptyPlugin]; ```
There is a core ecs plugin which builds on top of bevy_ecs. It allows you to supply your own systems and build schedules dynamically. It is possible to load and find new ecs systems in different dynamic libraries. You can register and instantiate demos which are collections of setup, update and render systems.
You can set up a new ecs demo by providing an initialisation function named after the demo this returns a ScheduleInfo for which systems to run:
```rust /// Init function for primitives demo
pub fn primitives(client: &mut Client
// fill out info
ScheduleInfo {
setup: systems![
"setup_primitives"
],
update: systems![
"update_cameras",
"update_main_camera_config"
],
render_graph: "mesh_debug"
}
} ```
You can supply setup systems to add entities into a scene, when a dynamic code reload happens the world will be cleared and the setup systems will be re-executed. This allows changes to setup systems to appear in the live client. You can add multiple setup systems and they will be executed concurrently.
```rust
pub fn setupcube(
mut device: bevyecs::changedetection::ResMut
let pos = Mat4f::from_translation(Vec3f::unit_y() * 10.0);
let scale = Mat4f::from_scale(splat3f(10.0));
let cube_mesh = hotline_rs::primitives::create_cube_mesh(&mut device.0);
commands.spawn((
Position(Vec3f::zero()),
Velocity(Vec3f::one()),
MeshComponent(cube_mesh.clone()),
WorldMatrix(pos * scale)
));
} ```
You can specify render graphs in pmfx that set up views, which get dispatched into render functions. All render systems run concurrently on the CPU, the command buffers they generate are executed in an order determined by the pmfx render graph and it's dependencies.
```rust
pub fn rendermeshes(
pmfx: &bevyecs::prelude::Res
let fmt = view.pass.get_format_hash();
let mesh_debug = pmfx.get_render_pipeline_for_format(&view.view_pipeline, fmt)?;
let camera = pmfx.get_camera_constants(&view.camera)?;
// setup pass
view.cmd_buf.begin_render_pass(&view.pass);
view.cmd_buf.set_viewport(&view.viewport);
view.cmd_buf.set_scissor_rect(&view.scissor_rect);
view.cmd_buf.set_render_pipeline(&mesh_debug);
view.cmd_buf.push_render_constants(0, 16 * 3, 0, gfx::as_u8_slice(camera));
// make draw calls
for (world_matrix, mesh) in &mesh_draw_query {
view.cmd_buf.push_render_constants(1, 16, 0, &world_matrix.0);
view.cmd_buf.set_index_buffer(&mesh.0.ib);
view.cmd_buf.set_vertex_buffer(&mesh.0.vb, 0);
view.cmd_buf.draw_indexed_instanced(mesh.0.num_indices, 1, 0, 0, 0);
}
// end / transition / execute
view.cmd_buf.end_render_pass();
Ok(())
} ```
You can also supply your own update systems to animate and move your entities, these too are all executed concurrently.
rust
fn update_cameras(
app: Res<AppRes>,
main_window: Res<MainWindowRes>,
mut query: Query<(&mut Position, &mut Rotation, &mut ViewProjectionMatrix), With<Camera>>) {
let app = &app.0;
for (mut position, mut rotation, mut view_proj) in &mut query {
// ..
}
}
Systems can be imported dynamically from different plugins, in order to do so they need to be hooked into a function which can be located dynamically by the ecs plugin. In time I hope to be able to remove this baggage and be able to #[derive()] them.
You can implement a function called get_demos_<lib_name>, which returns a list of available demos inside a plugin named <lib_name> and get_system_<lib_name> to return bevy_ecs::SystemDescriptor of systems that can then be looked up by name. The ecs plugin will search for systems by name within all other loaded plugins, so you can build and share functionality.
```rust /// Register demo names
pub fn getdemosecsdemos() -> Vec
// ..
]
}
/// Register plugin system functions
pub fn getsystemecsdemos(name: String, viewname: String) -> Option
By default all systems in a particular group will be executed asyncronsly and the groups will be executed in-order:
SystemSets::Update - Use this to animate and move entities, perform logic adn so forth.SystemSets::Batch - Use this to batch data such as baking world matrices, culling or update buffers ready for rendering.SystemSets::Render - Used to render entities and make draw calls.Any render functions are automatically added to the Render system set, but you can choose to create your own sets or add things into the pre-defined SystemSets. There are some core oprations which will happen but you can define your own and order execution as follows:
```rust // updates "rotatemeshes" => systemfunc![ rotatemeshes .inbase_set(CustomSystemSet::Animate) .after(SystemSets::Update) ],
// batches "batchworldmatrixinstances" => systemfunc![ draw::batchworldmatrix_instances .after(SystemSets::Batch) ], ```
You can supply your own serialisable plugin data that will be serialised with the rest of the user_config and can be grouped with your plugin and reloaded between sessions.
```rust /// Seriablisable user info for maintaining state between reloads and sessions
pub struct SessionInfo {
pub activedemo: String,
pub maincamera: Option
// the client provides functions which can serialise and deserialise this data for you fn updateuserconfig(&mut self) { // find plugin data for the "ecs" plugin self.sessioninfo = client.deserialiseplugin_data("ecs");
//.. make updates to your data here
// write back session info which will be serialised to disk and reloaded between sessions
client.serialise_plugin_data("ecs", &self.session_info);
} ```
You can use hotline as a library inside the plugin system or on its own to use the low level abstractions and modules to create windowed applications with a graphics api backend. Here is a small example:
```rust // include prelude for convenience use hotline_rs::prelude::*;
pub fn main() -> Result<(), hotliners::Error> { // Create an Application let mut app = osplatform::App::create(os::AppInfo { name: String::from("triangle"), window: false, numbuffers: 0, dpiaware: true, });
// Double buffered
let num_buffers = 2;
// Create an a GPU Device
let mut device = gfx_platform::Device::create(&gfx::DeviceInfo {
render_target_heap_size: num_buffers,
..Default::default()
});
// Create main window
let mut window = app.create_window(os::WindowInfo {
title: String::from("triangle!"),
..Default::default()
});
/// Create swap chain
let swap_chain_info = gfx::SwapChainInfo {
num_buffers: num_buffers as u32,
format: gfx::Format::RGBA8n,
..Default::default()
};
let mut swap_chain = device.create_swap_chain::<os_platform::App>(&swap_chain_info, &window)?;
/// Create a command buffer
let mut cmd = device.create_cmd_buf(num_buffers);
// Run main loop
while app.run() {
// update window and swap chain
window.update(&mut app);
swap_chain.update::<os_platform::App>(&mut device, &window, &mut cmd);
// build command buffer and make draw calls
cmd.reset(&swap_chain);
// Render command can go here
// ..
cmd.close()?;
// execute command buffer
device.execute(&cmd);
// swap for the next frame
swap_chain.swap(&device);
}
// must wait for the final frame to be completed so it is safe to drop GPU resources.
swap_chain.wait_for_last_frame();
Ok(());
} ```
The gfx module provides a modern graphics API loosely following Direct3D12 with Vulkan and Metal compatibility in mind. If you are familiar with those API's it should be straight forward, but here is a quick example of how to do some render commands:
```rust
// create a buffer
let info = gfx::BufferInfo {
usage: gfx::BufferUsage::Vertex,
cpuaccess: gfx::CpuAccessFlags::NONE,
format: gfx::Format::Unknown,
stride: std::mem::sizeof::
// create shaders and a pipeline let vscfilepath = hotliners::getdatapath("shaders/triangle/vsmain.vsc"); let pscfilepath = hotliners::getdatapath("shaders/triangle/psmain.psc");
let vscdata = fs::read(vscfilepath)?; let pscdata = fs::read(pscfilepath)?;
let vscinfo = gfx::ShaderInfo { shadertype: gfx::ShaderType::Vertex, compileinfo: None }; let vs = device.createshader(&vscinfo, &vscdata)?;
let pscinfo = gfx::ShaderInfo { shadertype: gfx::ShaderType::Vertex, compileinfo: None }; let fs = device.createshader(&pscinfo, &pscdata)?;
// create the pipeline itself with the vs and fs let pso = device.createrenderpipeline(&gfx::RenderPipelineInfo { vs: Some(&vs), fs: Some(&fs), inputlayout: vec![ gfx::InputElementInfo { semantic: String::from("POSITION"), index: 0, format: gfx::Format::RGB32f, inputslot: 0, alignedbyteoffset: 0, inputslotclass: gfx::InputSlotClass::PerVertex, steprate: 0, }, gfx::InputElementInfo { semantic: String::from("COLOR"), index: 0, format: gfx::Format::RGBA32f, inputslot: 0, alignedbyteoffset: 12, inputslotclass: gfx::InputSlotClass::PerVertex, steprate: 0, }, ], descriptorlayout: gfx::DescriptorLayout::default(), rasterinfo: gfx::RasterInfo::default(), depthstencilinfo: gfx::DepthStencilInfo::default(), blendinfo: gfx::BlendInfo { alphatocoverageenabled: false, independentblendenabled: false, rendertarget: vec![gfx::RenderTargetBlendInfo::default()], }, topology: gfx::Topology::TriangleList, patchindex: 0, pass: swapchain.getbackbufferpass(), })?;
// build command buffer and make draw calls cmd.reset(&swap_chain);
// manual transition handling cmd.transitionbarrier(&gfx::TransitionBarrier { texture: Some(swapchain.getbackbuffertexture()), buffer: None, statebefore: gfx::ResourceState::Present, stateafter: gfx::ResourceState::RenderTarget, });
// render pass approach is used, swap chain automatically creates some for us cmd.beginrenderpass(swapchain.getbackbufferpassmut()); cmd.setviewport(&viewport); cmd.setscissor_rect(&scissor);
// set state for the draw cmd.setrenderpipeline(&pso); cmd.setvertexbuffer(&vertexbuffer, 0); cmd.drawinstanced(3, 1, 0, 0); cmd.endrenderpass();
// manually transition cmd.transitionbarrier(&gfx::TransitionBarrier { texture: Some(swapchain.getbackbuffertexture()), buffer: None, statebefore: gfx::ResourceState::RenderTarget, stateafter: gfx::ResourceState::Present, });
// execute command buffer cmd.close()?; device.execute(&cmd);
// swap for the next frame swap_chain.swap(&device); ```
Pmfx builds on top of the gfx module to make render configuration more ergonomic, data driven and quicker to develop with. You can use the pmfx module and pmfx data to configure render pipelines in a data driven way. The pmfx-shader repository has more detailed information and is currently undergoing changes and improvements but it now supports a decent range of features.
You can supply jsn config files to specify render pipelines, textures (render targets), views (render pass with cameras) and render graphs. Useful defaults are supplied for all fields and combined with jsn inheritance it can aid creating many different render strategies with minimal repetition.
jsonnet
textures: {
main_colour: {
ratio: {
window: "main_window",
scale: 1.0
}
format: "RGBA8n"
usage: ["ShaderResource", "RenderTarget"]
samples: 8
}
main_depth(main_colour): {
format: "D24nS8u"
usage: ["ShaderResource", "DepthStencil"]
samples: 8
}
}
views: {
main_view: {
render_target: [
"main_colour"
]
clear_colour: [0.45, 0.55, 0.60, 1.0]
depth_stencil: [
"main_depth"
]
clear_depth: 1.0
viewport: [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0]
camera: "main_camera"
}
main_view_no_clear(main_view): {
clear_colour: null
clear_depth: null
}
}
pipelines: {
mesh_debug: {
vs: vs_mesh
ps: ps_checkerboard
push_constants: [
"view_push_constants"
"draw_push_constants"
]
depth_stencil_state: depth_test_less
raster_state: cull_back
topology: "TriangleList"
}
}
render_graphs: {
mesh_debug: {
grid: {
view: "main_view"
pipelines: ["imdraw_3d"]
function: "render_grid"
}
meshes: {
view: "main_view_no_clear"
pipelines: ["mesh_debug"]
function: "render_meshes"
depends_on: ["grid"]
}
wireframe: {
view: "main_view_no_clear"
pipelines: ["wireframe_overlay"]
function: "render_meshes"
depends_on: ["meshes", "grid"]
}
}
}
When pmfx is built, shader source is generated along with an info file that contains useful reflection information to be used at runtime. Based on shader inputs and usage, descriptor layouts and vertex layouts are automatically generated.
There are a few standalone examples of how to use the lower level components of hotline (gfx, app, av). You can build and run these as follows:
```text // build examples cargo build --examples
// make sure to build data .hotline-datapmbuild.cmd win32-data
// run a single sample cargo run --example triangle ```
There are standalone tests and client/plugin tests to test graphics API features. This requires a test runner which has a GPU and is not headless, so I am using my home machine as a self-hosted actions runner. You can run the tests yourself but because of the requirement of a GPU device and plugin loading the tests need to be ran single threaded.
text
cargo test -- --test-threads=1
This is wrapped into pmbuild so you can also run:
text
pmbuild test
Contributions of all kinds are welcome, you can make a fork and send a PR if you want to submit small fixes or improvements. Anyone interested in being more involved in development I am happy to take on people to help with the project of all experience levels, especially people with more experience in Rust. You can contact me if interested via Twitter or Discord.