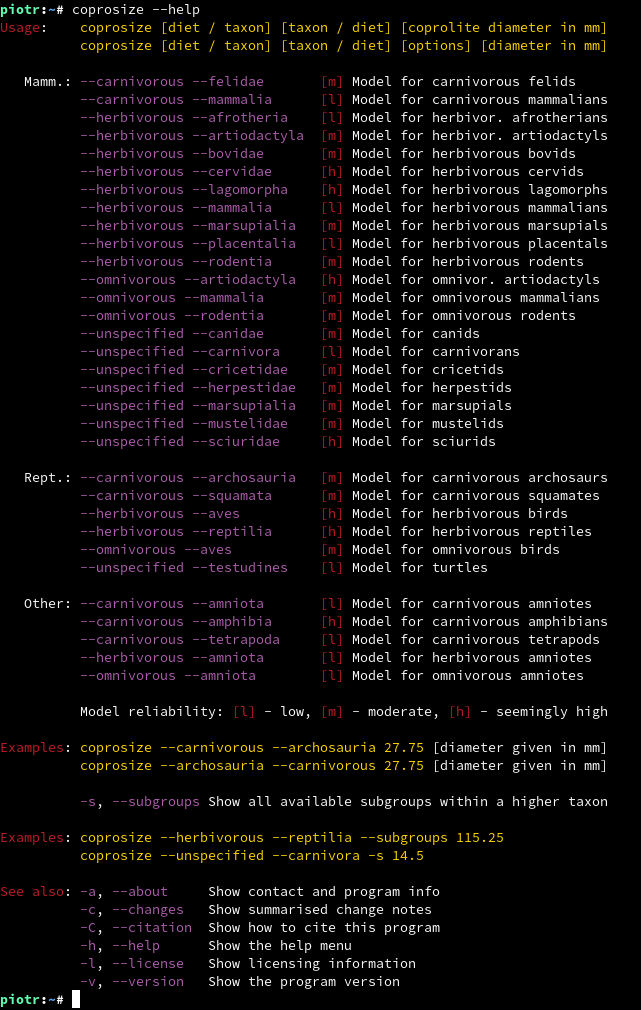
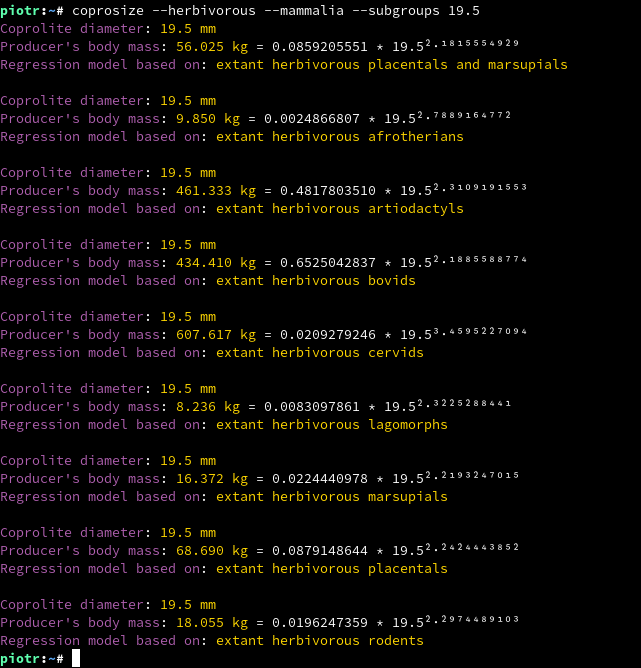
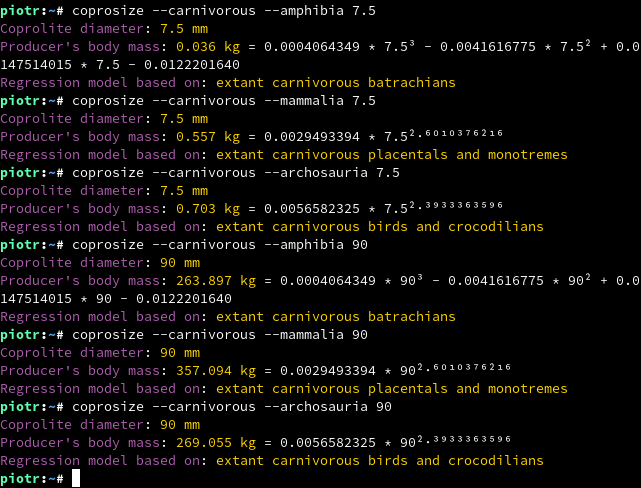
coprosize employs power, exponential and cubic regression models allowing to estimate the producer's body mass based on coprolite diameter. Models can be chosen accordingly to the supposed producer's taxon (at this stage of program development, only tetrapod models are implemented) and its diet type (carnivorous, herbivorous, omnivorous, unspecified). Implemented regression formulae are provided in Supplement 1. Regression models and constructed based on the data given in Supplement 2. Scat diameters and body masses.
As it is aimed for science, coprosize is written in Rust. The reasons for this choice are (1) the high code correctness guaranteed by Rust, (2) to ensure that each program version will be accessible in the registry 'in perpetuity' and (3) that each program version will remain easily installed and cross-platform 'in perpetuity', thanks to the Rust's strict policy of backwards compatibility.
[keywords (en-AU): animal scats, archaeology, biology, body mass, body size, coprolites, dung, fossil faeces, fossils, geology, ichnology, palaeontology, scientific computing, weight; (en-US): fossil feces, paleontology]

Please, always refer to a specific program version--implemented formulae are subject to change if new data are available (or simply studied by the author) or bugs of any kind are detected. Although coprosize is designed with the needs of a user in mind, you are perfectly OK to use my models in your study without really installing it as long as you cite this computer program as the original source:
Bajdek, P., 2023. coprosize (version 1.0.3). [computer software] https://github.com/piotrbajdek/coprosize
You are also OK to modify and fork coprosize under terms of the MIT License. It is moreover possible to link against coprosize using its library as a dependency for other bioinformatics projects (see public functions). The usage is best explained by example:
Add to your Cargo.toml file:
[dependencies]
coprosize = "1.0.3"
Put in your src/main.rs file:
fn main() {
let diameter = "9"; // diameter as &str
coprosize::herbivorous_rodentia(diameter);
println!();
coprosize::omnivorous_rodentia(diameter);
println!();
println!("Source of the above models:");
println!();
coprosize::citation();
}
The above program will reuse the internal library of coprosize. Note that the 'diameter' must be given as a string slice (of numbers and optionally including a dot)--the library won't work receiving neither an integer nor a floating point.
coprosize should run smoothly on Windows and macOS, and can be installed by the use of cargo. Yet, it is being developed and primarily tested on Fedora Linux.
coprosize v1.0.3:
– Was successfully tested on Fedora Linux 37, openSUSE Tumbleweed, and Ubuntu 22.10.
– Failed to run on Mageia 8 due to an old glibc version (required ≥2.34).
[recommended for programmers]
1. Install from crates.io by the use of cargo:
cargo install coprosize
By default, the file will be downloaded to .cargo/bin/, a hidden folder in your home directory.
2a. For convenience, you will probably want to copy coprosize to /usr/bin/ as in Method 2 (3a, 3b).
2b. Alternatively, add ~/.cargo/bin directory to your PATH variable (can be set up by rustup).
1. Download the distro-independent binary of coprosize from GitHub.
2. Make the file executable:
sudo chmod +x ./coprosize
3a. On most Linux distros, install coprosize via copying the binary to /usr/bin/:
sudo cp coprosize /usr/bin/
3b. On Fedora Silverblue / Kinoite:
sudo cp coprosize /var/usrlocal/bin/
[recommended for most users]
Distro-specific packages are also available for download for .rpm- and .deb-based Linux distros. Installation instructions:
Fedora Linux / RHEL / openSUSE:
sudo rpm -i coprosize-1.0.3-1.x8664.rpm_
Fedora Silverblue / Kinoite:
rpm-ostree install coprosize-1.0.3-1.x8664.rpm_
Ubuntu:
sudo dpkg -i coprosize1.0.3amd64.deb
Download and unpack the coprosize source from GitHub. Then, build and install the program:
cargo build --release && sudo cp target/release/coprosize /usr/bin/